Navigating the HSC exams can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding and responding to the nuances of the seemingly endless HSC verbs. However, understanding each of the NESA key words provides you a meaningful indicator of how much to write, as well as the depth and sophistication required for a high scoring response.
For certain key words, the literal or dictionary meanings is not enough. Below we break down the glossary of key words NESA has provided to understand the relevant details of each term, allowing us to note differences in what each individual question is asking for in an exam setting.
Account
“Account for: state reasons for, report on. Give an account of: narrate a series of events or transactions”
What does this really mean? “Account for” means to provide explanations, reasons, or justifications for something.
How do I respond to this? When answering a question led by the verb “account”, it is critical to focus on
- The reason(s) for the occurrence of the subject.
- Reporting the cause and effect of what has occurred.
- Narrating the series of events or transactions.
Example:
Australia’s gini coefficient for income distribution has fallen from 0.329 in 2009/10 to 0.324 in 2019/20, Account for this trend in the Australian economy. (2 marks) - Project HSC Economics
Sample Answer:
The decrease in the gini coefficient in Australia is representative of a decline in income inequality in the economy (1). This may be due to expansionary monetary policy noted by a decline in the cash rate from 2.5% in 2014 to 0.1% in November 2020, which has reduced debt repayments by lower income borrowers to higher income lenders, leading to an improvement in the distribution of income (2 and 3).
Analyse
“Identify components and the relationship between them; draw out and relate implications”
What does this really mean?
“Analyse” questions ask that you examine something in detail, break it down into its constituent parts, and investigate its components to gain a deeper understanding.
How do I respond to this?
“Analyse” questions are usually weighted more heavily, and hence demand more in how they are answered. Such important elements are
- Identify the components of an occurrence, and the relationship between these components.
- Using such relationships, draw out and relate implications.
- Provide a comprehensive examination, considering contrasting viewpoints if necessary.
- Optionally support analysis with evidence or examples to strengthen arguments.
Example:
Analyse the economic and social costs of an increase in income inequality. (5 marks) - HSC exam 2023
Sample Answer:
An increase in income inequality exacerbates economic and social disparities within a society. (1) Economically, it leads to reduced consumer spending among lower-income households, limiting aggregate demand and economic growth. Socially, it deepens divisions, fostering feelings of resentment and alienation among those marginalized by the unequal distribution of wealth. (2) Furthermore, it can hinder social mobility, perpetuating cycles of poverty and limiting opportunities for upward mobility. Additionally, income inequality can strain social cohesion, leading to increased crime rates and political instability as marginalized groups seek to address their grievances. (3)
Apply
“Use, utilise, employ in a particular situation”
What does this really mean?
An “apply” question requires you to extend your knowledge of a certain theory or formula to a different context or scenario.
How do I respond to this?
It is important to
- Briefly summarise the original theory/formula.
- Use relevant details to show how this concept can be transferred to a different situation and still remain functional.
Appreciate
“Make a judgement about the value of”
What does this really mean?
In exam questions, ‘Appreciate’ typically entails understanding the significance, value, or implications of a given concept, idea, or situation.
How do I respond to this?
- Briefly outline the concept that the question is focused on.
- Demonstrate awareness of its importance or relevance, within both a specific and broader context.
- Support your appreciation with relevant evidence or examples where applicable.
Assess
“Make a judgement of value, quality, outcomes, results or size”
What does this really mean?
‘Assess’ in exam questions requires evaluating or judging the quality, significance, or effectiveness of a given concept, idea, or situation.
How do I respond to this?
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the topic under consideration.
- Judge its significance or effectiveness based on specified criteria.
- Consider multiple perspectives or viewpoints.
- Provide a balanced assessment, acknowledging both positive and negative aspects.
- Support your assessment with evidence, examples, or reasoning.
Note that you do not need to make a black and white judgement regarding whether the positive aspects outweigh the negative impacts. It is important to make a relative judgement; meaning that your final assessment can be that the topic under consideration is “partially ineffective”, “somewhat effective”, etc.
Example:
Assess the impact of continuing world economic development on environmental sustainability. (5 marks) - Project HSC Economics
Sample Answer:
Historical world economic development has been associated with increased population growth and consumption rates from rising incomes. This rise in output necessitated the use of increased resources at an unsustainable rate, reducing environmental sustainability. (1) Specifically developing and emerging economies engaged in the use of poor environmental practices in accordance with industrialization, to facilitate rising growth and economic development. This is evident with the rapid increase in CO2 per capita in the Chinese economy from 1.5 tonnes / capita (1980) to 7.0 tonnes / capita (2011) alongside an average 9-10% growth from 1980 to 2008. These increases in CO2 emissions contribute to air pollution and worsening environmental sustainability. (2)
Recent world economic development has been focused towards improvements in environmental sustainability through international agreements as evident with Paris Agreement (2015). Through this 195 nations signed on to limit rising temperatures to 1.5-2 degrees celsius by 2030(5) through coordinating environmental policies. However, as of September 2021 only I nation (Gambia) was meeting their Paris trajectory.(3) Therefore, continuing world economic development has overall worsened environmental sustainability. (4)
Calculate
“Ascertain/determine from given facts, figures or information”
What does this really mean?
‘Calculate’ questions are usually used in math or science, and ask that you use numbers or equations to solve for a solution.
Example:
The data shows the balance of payments for an economy under a floating exchange rate.
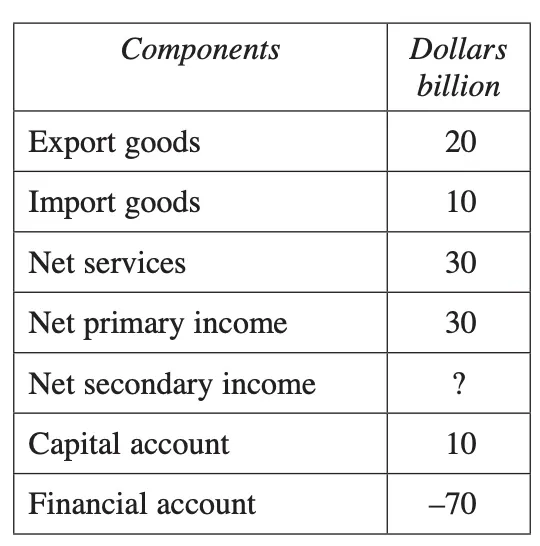


Calculate the value of net secondary income (dollars billion) for the balance of payments data shown. - HSC Economics Exam 2023
Sample Answer:
- Step 1: Calculate BOGS: BOGS =$40bn
- Step 2: Calculate KAFA: = $-60bn
- Step 3: Solve for NSY:
- BOGS+NPY+NSY=-1(KAFA)
- $40bn+$30bn+NSY=$60bn
- Therefore NSY= $-10bn
Clarify
“Make clear or plain”
What does this really mean?
“Clarify” involves making something clear or understandable. In exam questions, this often requires you to provide explanations or further details.
How do I respond to this?
- Provide a clear and concise explanation of the subject matter of the question.
- Use relevant examples, analogies, or illustrations to further elucidate the explanation and ensure clarity for the reader.
- Anticipate potential areas of misunderstanding and address them preemptively to leave no room for ambiguity.
Classify
“Arrange or include in classes/categories”
What does this really mean?
“Classify” involves categorising or organising elements into groups based on shared characteristics, usually according to specific criteria.
How do I respond to this?
- Begin by understanding the criteria or characteristics by which the items need to be classified, as specified in the question.
- Identify the items or elements that need to be classified and analyse their characteristics to determine appropriate groupings.
- Clearly state the criteria used for classification and provide rationale for each grouping to justify the classification process.
Compare
“Show how things are similar or different”
What does this really mean?
“Compare” involves examining similarities and differences between two or more items, concepts, or situations.
How do I respond to this?
In exam questions, this often requires you to analyse and evaluate the relationships between the elements being compared.
- Begin by identifying the items, concepts, or situations that need to be compared as specified in the question.
- Analyse the key characteristics, attributes, or features of each item, concept, or situation to determine similarities and differences. This may also involve finding both positive and negative elements of each of the subjects.
- Organise your comparison by clearly delineating between similarities and differences using a structured approach such as a table, Venn diagram, or paragraph format.
- Provide specific examples, evidence, or illustrations to support your comparisons and enhance clarity.
- Evaluate the significance of the similarities and differences identified, highlighting any implications or insights gained from the comparison.
Construct
“Make; build; put together items or arguments”
What does this really mean?
“Construct” involves building or creating something based on given instructions, criteria, or guidelines. This will likely require you to develop or produce a response, solution, or product.
How do I respond to this?
- Begin by understanding the task or requirements outlined in the question, including any instructions, criteria, or guidelines provided.
- Follow the specified instructions, criteria, or guidelines meticulously while constructing your final response, ensuring you address necessary subject matter and adhere to guidelines/stimulus whilst constructing your arguments.
Contrast
“Show how things are different or opposite”
What does this really mean?
“Contrast” involves highlighting differences between two or more items, concepts, or situations.
How do I respond to this?
- Begin by identifying the items, concepts, or situations that need to be contrasted as specified in the question.
- Analyse the key characteristics, attributes, or features of each item, concept, or situation to determine differences.
- Organise your response by clearly delineating between the differences using a structured approach such as a table, Venn diagram, or paragraph format.
- Provide specific examples, evidence, or illustrations to support your contrasts and enhance clarity.
- Evaluate the significance of the differences identified, highlighting any implications or insights gained from the contrast.
Critically (analyse/evaluate)
“Add a degree or level of accuracy depth, knowledge and understanding, logic, questioning, reflection and quality to (analyse/evaluate)”
What does this really mean?
“Critically Analyse/Evaluate” involves examining a topic, issue, or argument in-depth, considering its strengths, weaknesses, implications, and significance. This often requires you to assess and judge the merits of a particular perspective, theory, or assertion.
How do I respond to this?
- Break down the topic into its constituent parts and analyse each component thoroughly.
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the topic, argument, theory, or evidence presented. Consider different perspectives, weighing their validity and significance.
- Reflect on the broader implications or consequences of the topic or issue being analysed. This may involve discussing potential impacts, implications for different stakeholders, or broader societal, ethical, or practical considerations.
- Based on your analysis and evaluation, formulate a well-supported judgment or conclusion. Clearly articulate your stance and provide evidence or reasoning to support your viewpoint.
Deduce
“Draw conclusions”
What does this really mean?
“Deduce” involves drawing logical conclusions or inferences based on given information, evidence, or premises.
How do I respond to this?
- Identify the logical relationships and patterns within the information, evidence, or premises that can be used to draw conclusions or inferences.
- Use deductive reasoning to analyse the information, evidence, or premises and logically infer conclusions based on established principles, rules, or assumptions.
- Provide clear explanations or justifications for your deductions, demonstrating the reasoning process behind your conclusions.\
Define
“State meaning and identify essential qualities demonstrate”
What does this really mean?
Usually worth fewer marks, “Define” questions ask that you provide a clear and precise explanation or description of a term, concept, or idea.
Demonstrate
“Show by example”
What does this really mean?
“Demonstrate” involves showing or proving something through examples, evidence, or practical application.
How do I respond to this?
- Outline the concept or procedure that needs to be demonstrated as denoted by the question.
- Provide clear and concrete examples, evidence, or illustrations to showcase your understanding or proficiency in the required area.
- Explain the effect and impact of the concept or procedure.
Describe
“Provide characteristics and features”
What does this really mean?
“Describe” involves providing a detailed account of the meaning and function of a specific subject.
How do I respond to this?
- Identify the subject area, provide an outline of its function and purpose.
- Detail its specific features and functions.
Example:
Describe the relationship between the balance of the capital and financial account and the net income balance. (2 marks) - Project Academy HSC Economics
Sample Answer:
An increase in the capital and financial account surplus would result in an increase in the net income deficits, indicating an inverse relationship. This is because initial transactions such as an inflow of foreign direct investment would be recorded as a credit on the capital and financial account(1), and later transactions would be recorded as debits as outflows of equity repayments on the net income.(2)
Discuss
“Identify issues and provide points for and/or against”
What does this really mean?
“Discuss” involves exploring a topic, issue, or question in depth, considering different perspectives, arguments, or viewpoints.
How do I respond to this?
- Identify the topic, issue, or question that needs to be discussed as specified in the question.
- Provide a comprehensive overview of the topic, including any relevant background information or context necessary for understanding.
- Present different perspectives, arguments, or viewpoints on the topic, considering both supporting and opposing viewpoints.\
Example:
Discuss the economic consequences associated with a more inequitable distribution of income for the Australian economy. (4 marks) - Project HSC Economics
Sample Answer:
Income inequality can result in an incentive for low income earners to take certain actions in order to earn higher incomes, such as increased risk taking as an entrepreneur, productivity and hours worked. (1) (2) This can lead to increased aggregate supply and long term economic growth, benefiting the economy. Income inequality also results in more high income earners, who tend to have a high marginal to save (MPS) thereby leading to an increase in national savings. This reduced the need to undertake international borrowing to finance domestic investment. This improves net foreign debt as a percentage of GDP, improving external stability.(3)
Distinguish
“Recognise or note/indicate as being distinct or different from; to note differences between”
What does this really mean?
“Distinguish” involves identifying and highlighting the differences between two or more items, concepts, or ideas.
How do I respond to this?
- Begin by identifying the items, concepts, or ideas that need to be distinguished.
- Analyse the key characteristics of each item, concept, or idea to determine differences.
- If necessary, clearly delineate between the differences, providing specific examples, evidence, or illustrations to support your distinctions.\
Example:
Distinguish between a private cost and a social cost. (2 marks) - Project Academy HSC Economics
Sample Answer:
A private cost refers to the negative impact on the consumer or firm directly involved in the production or consumption of the good or service.(1) Whereas, a social cost refers to the private cost in addition to any negative impacts on the rest of society from the production or consumption of the good or service.(2)
Evaluate
“Make a judgement based on criteria; determine the value of”
What does this really mean?
“Evaluate” involves assessing and making judgments about the strengths, weaknesses, merits, or significance of something based on criteria or standards.
How do I respond to this?
- Identify the subject area.
- Define the criteria or standards against which the subject will be evaluated, considering factors such as relevance, reliability, validity, feasibility, and ethical considerations.
- Analyse the strengths and weaknesses of the subject based on the established criteria, providing evidence, examples, or reasoning to support your assessment.
- Draw reasoned conclusions and provide recommendations or judgments based on your evaluation.
Examine
“Inquire into”
What does this really mean?
“Examine” involves closely analysing or investigating a topic, issue, or question in detail.
How do I respond to this?
- Begin by identifying the specific topic, issue, or question that needs to be examined.
- Break down the topic into its constituent parts or elements, considering different perspectives, factors, or dimensions.
- Conduct a detailed analysis of each element.
- Evaluate the relationships between different parts or elements, identifying patterns or trends where applicable.
- Draw reasoned conclusions.
Explain
“Relate cause and effect; make the relationships between things evident; provide why and/or how”
What does this really mean?
“Explain” involves providing a clear and coherent account or clarification of a concept.
How do I respond to this?
- Begin by identifying the concept.
- Break down the topic into its constituent parts or elements.
- Provide a step-by-step explanation or description of the subject, using language that is clear, concise, and accessible to the intended audience.
- Use relevant evidence/examples if necessary.
Example:
Explain how fiscal policy and labour market policy can be used to reduce the gini coefficient. (4 marks) - Project HSC Economics
Sample Answer:
A reduction in the gini coefficient is associated with greater income equality.(1) Fiscal policy can improve income inequality by increasing welfare support to lower income earners. This will increase disposable incomes of lower quintiles and reduce disparity in income distribution.(2)
Labour market policy could be used to improve the distribution of income through an increase in centralisation in wage determination. This may involve an increase in the government’s role in determining wages, namely through increasing the safety net of income support for lower income earners. (3) This can further reduce the disparity in income distribution and reduce the gini coefficient.
Extract
“Choose relevant and/or appropriate details”
What does this really mean?
“Extract” involves selecting and isolating specific information, data, or details from a larger body of text, document, or source.
How do I respond to this?
- Begin by carefully reading the text, document, or source provided in the question, paying attention to the context and purpose of the extraction.
- Identify the specific information, data, or details that need to be extracted as specified in the question, focusing on key points that are relevant to the task at hand.
- Provide citations or references to indicate the source of the extracted information, acknowledging the original author or creator as appropriate.
Extrapolate
“Infer from what is known”
What does this really mean?
“Extrapolate” requires inferring or extending existing information, data, or trends to make predictions or draw conclusions about future/hypothetical scenarios.
How do I respond to this?
- Identify the patterns, relationships, or trends within the existing information or data that can be used to make predictions or draw conclusions.
- Use logical reasoning and critical thinking to extrapolate or extend these patterns or relationships to predict future outcomes or hypothetical scenarios.\
Identify
“Recognise and name”
What does this really mean?
“Identify” simply requires that you recognise and name an idea or information.
How do I respond to this?
- Recognise the concept or idea that is being specified.
- Name the subject of the question, and list characteristics and features if necessary.
Interpret
“Draw meaning from”
What does this really mean?
“Interpret” involves explaining or making sense of information, data, or texts.
How do I respond to this?
- Begin by carefully reading and understanding the source provided.
- Analyse the content and context of the information to identify patterns and relationships.
- Draw reasoned conclusions or interpretations based on your analysis, providing evidence.
Investigate
“Plan, inquire into and draw conclusions about”
What does this really mean?
“Investigate” entails systematically examining a specific topic to collect information, analyse evidence, and derive conclusions.
How do I respond to this?
- Identify and list the characteristics of the elements involved in your investigation.
- Explain the functions and purpose of each identified element.
- Describe potential impacts of each defined element of the investigation.
- Draw reasoned conclusions or findings based on your analysis, providing justification through relevant evidence.
Justify
“Support an argument or conclusion”
What does this really mean?
“Justify” asks that you provide valid reasons and evidence to support a particular position.
How do I respond to this?
- Begin by clearly stating the position that needs to be justified as specified in the question.
- Identify the key reasons and evidence supporting such position, considering factors such as validity and strength of argument.
- Present your justification in a logical and coherent manner. Use persuasive language and reasoning to strengthen your justification.
Outline
“Sketch in general terms; indicate the main features of”
What does this really mean?
“Outline” involves providing a brief summary or overview of a specified subject.
How do I respond to this?
- Identify and describe the specified subject in general terms.
- List the key features of the subject.
Predict
“Suggest what may happen based on available information”
What does this really mean?
“Predict” involves making educated guesses about future events based on existing information.
How do I respond to this?
- Analyse available information relevant to the question.
- Identify patterns, relationships, or trends within the existing information or data that may provide insights into future developments or outcomes.
- Use logical reasoning and critical thinking to extrapolate or extend these patterns.
- Provide justification or rationale for your predictions.
Propose
“Put forward (for example a point of view, idea, argument, suggestion) for consideration or action”
What does this really mean?
“Propose” involves suggesting an idea or solution for consideration.
How do I respond to this?
- Clearly identify the issue that needs to be addressed as specified in the question.
- Generate potential solutions or approaches to the problem, considering different perspectives.
- Evaluate the feasibility, effectiveness, and potential impact of each proposed solution.
- Select the most suitable proposal based on your evaluation, taking into account its potential to address the problem or challenge effectively and efficiently.
- Present your proposal in a clear and structured manner, outlining the key components and actions required for implementation.
Recall
“Present remembered ideas, facts or experiences”
What does this really mean?
“Recall” involves remembering or retrieving information, facts, or details, and presenting them in a logical answer.
How do I respond to this?
- Remember relevant details associated with the subject of the question
- Present them in a clear, logical manner.
Recommend
“Provide reasons in favour”
What does this really mean?
“Recommend” involves providing reasons in favour of a particular course of action.
How do I respond to this?
- Clearly identify the issue that needs to be addressed.
- Provide reasons that the specified course of action should be supported.
Recount
“Retell a series of events”
What does this really mean?
“Recount” involves or retelling a sequence of events in a logical order.
How do I respond to this?
- Clearly identify the event(s) in question.
- Organise your recount in a logical order.
- Provide relevant descriptions and evidence to support your retelling.
Summarise
“Express, concisely, the relevant details”
What does this really mean?
“Summarise” involves providing a concise and condensed overview of a topic, expressing the most relevant details.
How do I respond to this?
- Understand the information that you intend to summarise. This may involve reading a source.
- Identify the key information and main points.
- Use your own words to paraphrase and condense the information.
- Organise your summary in a logical and structured manner.
Focus on capturing the overarching theme or central message, rather than each minor detail.
Synthesise
“Putting together various elements to make a whole”
What does this really mean?
“Synthesise” involves combining multiple sources of information, ideas, or perspectives to generate new insights into a given topic.
How do I respond to this?
- Identify the various sources of information, ideas, or perspectives relevant to the topic at hand. These may be theories, texts, documents, etc.
- Evaluate each source critically, extracting the main concepts whilst considering overarching strengths, weaknesses and implications.
- Identify common themes, patterns, or relationships that emerge across the different source.
- Integrate the information from the various sources into a cohesive and original synthesis that offers new insights/interpretations.
- If necessary, provide justification/reasoning for your synthesis.